by LAUREN CODLING
INFORMED conversations with loved ones could be essential to increase vaccine take-up in some ethnic minority communities, a poll suggested last month.
New research by the British Red Cross (BRC) found that Britons from ethnic minority backgrounds are nearly twice as likely to get information on the vaccine from friends and family. Ethnic minorities are much more likely to have discussed their decision about whether to have the vaccine with extended family, the charity revealed.
According to its findings, 81 per cent of people from BAME communities said they would trust information from their family, a higher figure than when it came to the government (66 per cent) and the mainstream media (50 per cent).
The study is the latest of several which have analysed the vaccine take up within BAME communities. Analysis from the Office for National Statistics in January showed eight per cent of 460 Asian or Asian British adults said they would be unlikely to get a jab.
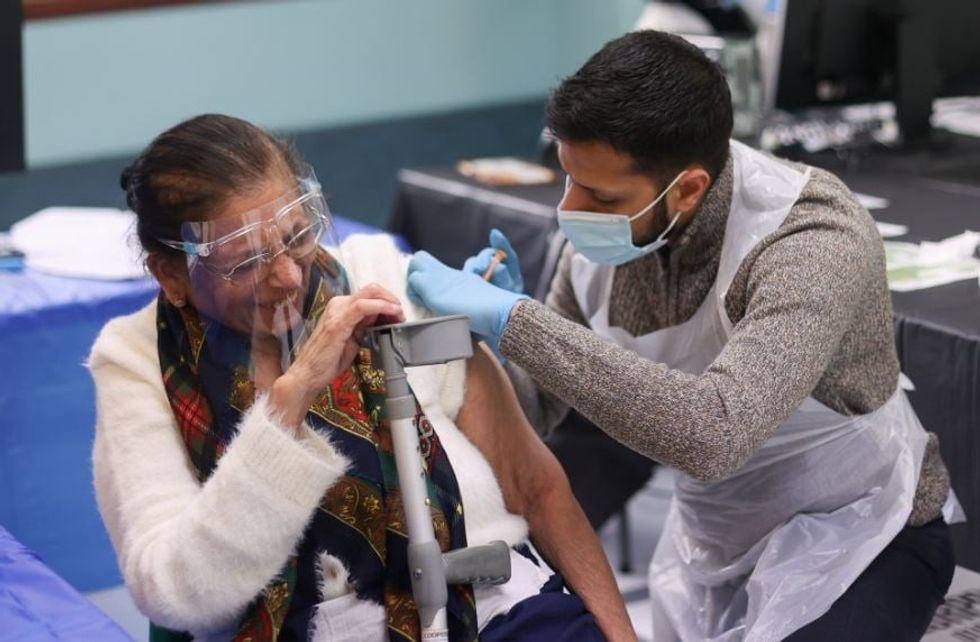
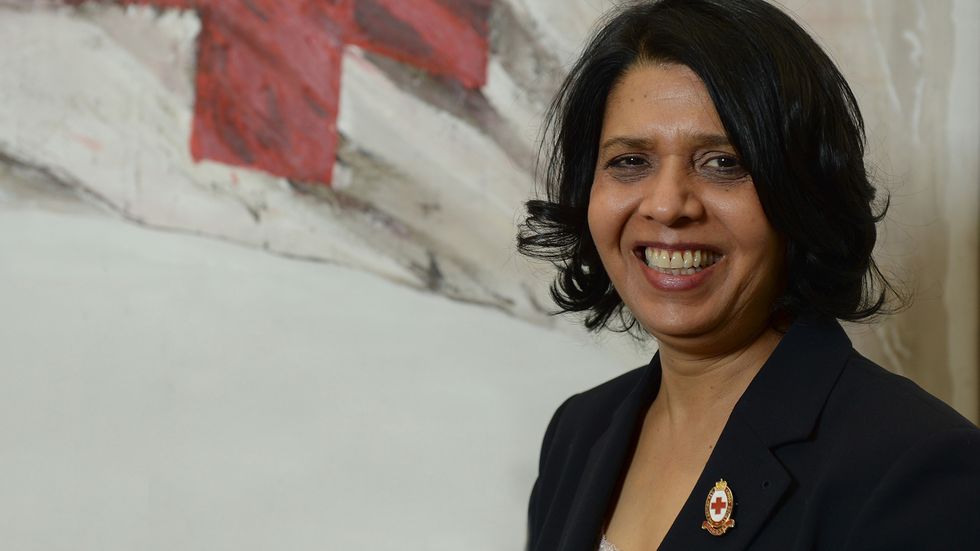
The BRC said family conversations could be key to tackling the hesitancy within some groups. Vice-chair of the BRC, professor Geeta Nargund, stressed the importance of people receiving accurate facts about the vaccine. “There has been a lot of false information circulating, in particular among BAME communities,” she told Eastern Eye on Monday (8). “Our research showed 62 per cent of BAME people had seen something encouraging them to not have the vaccine, and this can be very confusing for people to navigate.
“Talking about the vaccine saves lives and it is a vital way to protect and save others, including your loved ones.”
Data also found that vaccine hesitancy is higher among some ethnic minority communities – but not all. Outright rejection was highest among respondents identifying as Pakistani, black African and black Caribbean. “Potential reasons for higher hesitancy could be that these three groups are far more likely to have seen information encouraging them to not have the vaccine,” Nargund said. “Being more likely to have seen this content is likely to have an effect.”
However, the research found Indian (85 per cent) communities are just as likely to have already had/planning to have the vaccine as the UK average (87 per cent).
As well as her role at the BRC, Nargund is also a senior NHS consultant. As a healthcare professional, she acknowledged how important it is to speak to patients on any concerns they have regarding the vaccine. Many people want to check the accuracy of some of the information they have seen and talk through it, she added.

A common but false concern is that the vaccine causes infertility. “Speaking as a medical professional in this field, there is no biological or logical reason for this and there is no evidence for this,” she said.
Another concern is about the vaccine ingredients, particularly whether it contains animal products or if it is halal. “The vaccine does not contain any animal products – it’s suitable for vegetarians and vegans,” Nargund said. All of the current vaccines have been approved by the British Islamic Medical Association, Hindu Council UK and the Board Deputy of Religious Jews, she added.
Additional analysis found people from BAME backgrounds are over twice as likely to have spoken to family and friends about their vaccine concerns (31 per cent, compared to the national average of 14 per cent). They are also much more likely to have seen or heard information encouraging them not to have the vaccine (62 per cent compared to 42 per cent of the national average).
One in four of BAME respondents said that Covid-19 has caused tension in their family because of differing opinions, while 17 per cent had fallen out with family and friends because of their belief about the vaccine. The poll coincides with the launch of a BRC campaign designed to tackle vaccine hesitancy.
For more information, see: redcross.org.uk/coronavirus-vaccine