In recent years, the emergence and spread of vector-borne diseases transmitted by mosquitoes, such as Zika virus and West Nile virus, have highlighted the importance of effective pest and mosquito control strategies. As these diseases continue to pose significant threats to public health and well-being, researchers, policymakers, and pest management professionals are exploring innovative approaches to mitigate the risks associated with mosquito-borne illnesses. Let's delve into the evolving landscape of pest and mosquito control, from emerging threats to groundbreaking innovations.
The Rise of Vector-Borne Diseases
Vector-borne diseases, including those transmitted by mosquitoes, are a growing concern worldwide. Mosquito-borne illnesses such as Zika virus, West Nile virus, dengue fever, and chikungunya pose significant risks to human health, causing a range of symptoms from mild fever to severe neurological complications. Climate change, urbanization, globalization, and other factors contribute to the spread of these diseases, creating challenges for public health authorities and pest management professionals like Elite Pest and Mosquito Control.
Understanding Mosquito Biology and Behavior
Mosquitoes are complex organisms with intricate biology and behavior patterns that influence their ability to transmit diseases. Female mosquitoes require blood meals to produce eggs, making them vectors for pathogens that cause diseases in humans and animals. Understanding mosquito breeding habitats, feeding preferences and flight patterns is essential for developing targeted pest control strategies that disrupt mosquito populations and reduce disease transmission.
Traditional Pest Control Methods
Traditional pest control methods for mosquitoes have relied heavily on chemical pesticides, such as insecticides and larvicides, to kill adult mosquitoes and prevent mosquito larvae from developing into adults. While these methods can be effective in reducing mosquito populations in the short term, they pose risks to human health, non-target organisms, and the environment. Additionally, the overuse of chemical pesticides can lead to the development of pesticide-resistant mosquito populations, diminishing the effectiveness of control efforts.
Innovations in Mosquito Control
In response to the limitations of traditional pest control methods, researchers and pest management professionals are exploring innovative approaches to mosquito control that prioritize environmental sustainability and public health. Some of these innovations include:
- Biological Control: Biological control methods harness the natural enemies of mosquitoes, such as predatory fish, bacteria, fungi, and nematodes, to regulate mosquito populations. Biological control agents offer targeted and environmentally friendly solutions for reducing mosquito populations without relying on chemical pesticides.
- Genetic Control: Genetic control strategies, such as the release of genetically modified mosquitoes or the use of gene-editing technologies like CRISPR, aim to disrupt mosquito reproduction and reduce vector competence for disease transmission. These innovative approaches have the potential to suppress mosquito populations and mitigate the spread of mosquito-borne diseases.
- Sterile Insect Technique (SIT): The sterile insect technique involves mass-rearing and releasing sterile male mosquitoes into the environment to mate with wild females, leading to the suppression of mosquito populations over time. SIT has been successfully used to control mosquito populations in various regions and shows promise as a sustainable pest control strategy.
- Mosquito Traps and Monitoring Systems: Advanced mosquito traps and monitoring systems equipped with sensors, attractants, and data analytics capabilities enable real-time monitoring of mosquito populations and identification of high-risk areas for disease transmission. These tools facilitate targeted control efforts and enhance the effectiveness of mosquito control programs.
Community Engagement and Public Education
Effective mosquito control requires collaboration and engagement from the community. Public education campaigns that raise awareness about mosquito-borne diseases, mosquito biology, and prevention measures empower individuals to take proactive steps to protect themselves and their communities from mosquito bites. By promoting source reduction, personal protective measures, and community-based mosquito control initiatives, public health authorities and pest management professionals can reduce the risk of mosquito-borne diseases and improve public health outcomes.
Conclusion
From Zika to West Nile, emerging threats posed by mosquito-borne diseases underscore the need for innovative and sustainable pest control strategies. By understanding mosquito biology and behavior, exploring new technologies and approaches, and engaging communities in mosquito control efforts, researchers, policymakers, and pest management professionals can mitigate the risks associated with vector-borne diseases and protect public health. As the field of mosquito control continues to evolve, collaboration and innovation will be essential for addressing emerging threats and safeguarding communities from the impacts of mosquito-borne illnesses.
Top of Form
Bottom of Form
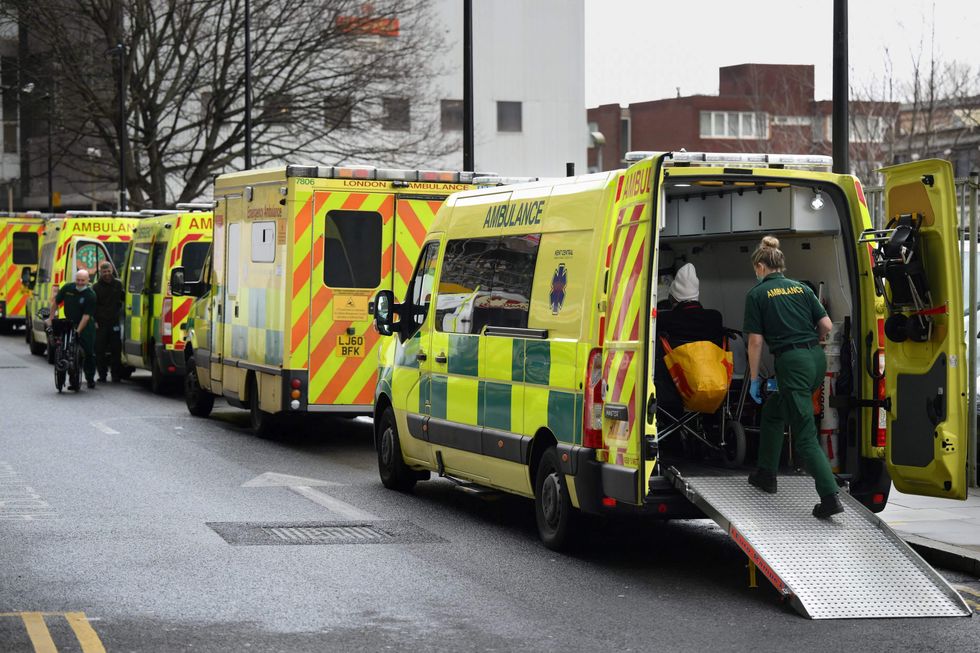




 'Sorting out the lack of social care in the community needs to be a priority'
'Sorting out the lack of social care in the community needs to be a priority'










 Jasvinder Sanghera (Photo by Jon Bond - WPA Pool/Getty Images)
Jasvinder Sanghera (Photo by Jon Bond - WPA Pool/Getty Images) Lord Kamlesh Patel
Lord Kamlesh Patel Lord Karan Bilimoria
Lord Karan Bilimoria Poppy Jaman
Poppy Jaman


