A European court ruling sparked an embarrassing climbdown for the British government by forcing the cancellation of Britain's first deportation flight of asylum seekers to Rwanda.
The British government expressed fury at the decision. But it is legally obliged to implement rulings by the Strasbourg-based European Court of Human Rights (ECHR), as a member of the Council of Europe and signatory of the European Convention on Human Rights. We take a look at the powers of the ECHR and why its verdicts apply to the UK.
What is the ECHR?
The ECHR is Europe's top human rights court and serves as a court of last instance in cases where all domestic avenues are exhausted.
It is part of the 46-member Council of Europe (COE) and oversees the implementation of the European Convention on Human Rights -- signed in 1950 and effective from 1953.
Rulings by the ECHR are not advisory, but legally binding and must, as such, be implemented by COE member states.
What did this ruling say?
The ECHR, responding to requests from human rights lawyers, issued a rarely used fast track "urgent interim measure" ordering the UK not to remove an Iraqi man, named as K.N., to Rwanda.
He had applied for asylum in the UK in May after crossing the Channel by boat.
"The Court grants such requests only on an exceptional basis, when the applicants would otherwise face a real risk of irreversible harm," it explained.
The measure effectively means that the UK cannot remove the man until a final decision in a domestic judicial review process. It prompted further appeals within the UK that then grounded the entire flight.
Why does this happen after Brexit?
The COE and the ECHR are separate from the European Union. Britain's exit from the Brussels-based bloc, therefore, has no impact on its membership of the COE, or its obligation to adhere to ECHR verdicts.
With its 46 members, the COE is a much wider body than the EU. In addition to the UK, other key COE members who do not belong to the EU include Turkey and Ukraine.
The only significant European states not to be members of the COE are Belarus and Russia. Belarus still employs the death penalty, a red line for membership of the body. Russia quit the COE and was then expelled anyway after its invasion of Ukraine this year.
What does the UK government say?
The British government has reacted with fury to Tuesday's ruling, with some even questioning Britain's future membership of the COE.
Work and Pension Secretary Therese Coffey told Sky News that she had "never known such a quick decision" from the ECHR and "the public will be surprised at European judges overruling British judges".
Prime Minister Boris Johnson appeared to question the human rights convention, saying "will it be necessary to change some rules to help us as we go along? It very well may be."
Ironically, Johnson's own maternal grandfather James Fawcett helped to write the convention and played a key role in an ECHR commission.
Can the UK defy ECHR rulings?
The rulings from the court are legally binding. But there have been issues concerning compliance by certain COE member states with its verdicts, especially Turkey and ex-member Russia which have flouted a number of rulings.
The ECHR had in December 2019 ordered Turkey to release leading civil society activist Osman Kavala, but he has remained behind bars.
The committee of ministers of the COE launched infringement proceedings against Turkey for only the second time in its history over the case. The process could ultimately see Turkey suspended or even expelled from the body.
The ECHR in February 2021 granted an interim measure ordering Russia to release opposition figure Alexei Navalny. Russia ignored the ruling and Navalny remained in jail.
The UK was also involved in a dispute with the ECHR for over a decade over a blanket ban on the right to vote for prisoners which was largely ended by a compromise plan submitted by the UK government in 2017.
(AFP)
















 All eyes on Donald Trump Jr and Bettina Anderson as their PDA grabs attention before Trump’s arrivalGetty Images
All eyes on Donald Trump Jr and Bettina Anderson as their PDA grabs attention before Trump’s arrivalGetty Images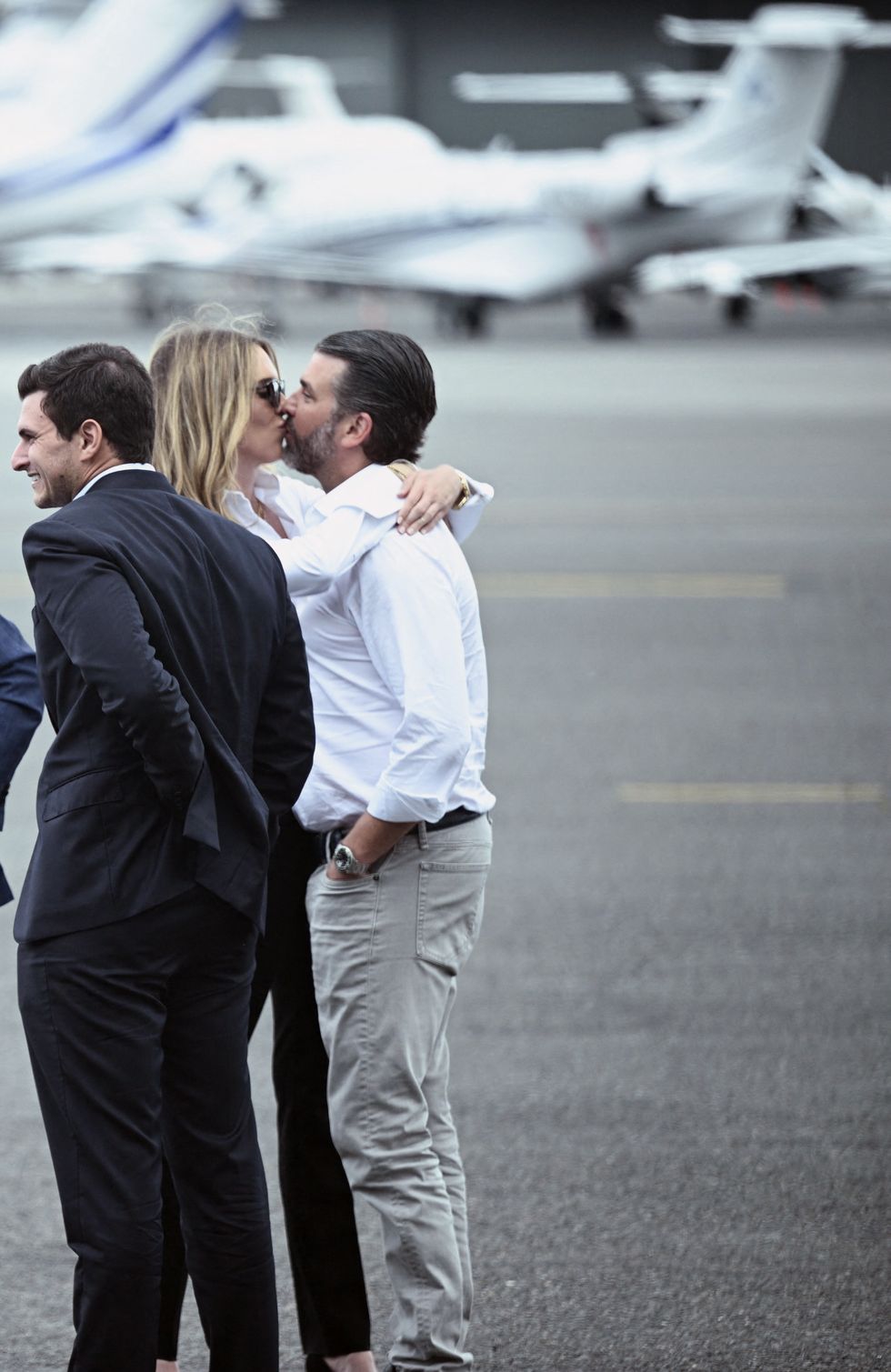  Donald Trump Jr and girlfriend Bettina Anderson steal the spotlight with PDA at New Jersey airportGetty Images
Donald Trump Jr and girlfriend Bettina Anderson steal the spotlight with PDA at New Jersey airportGetty Images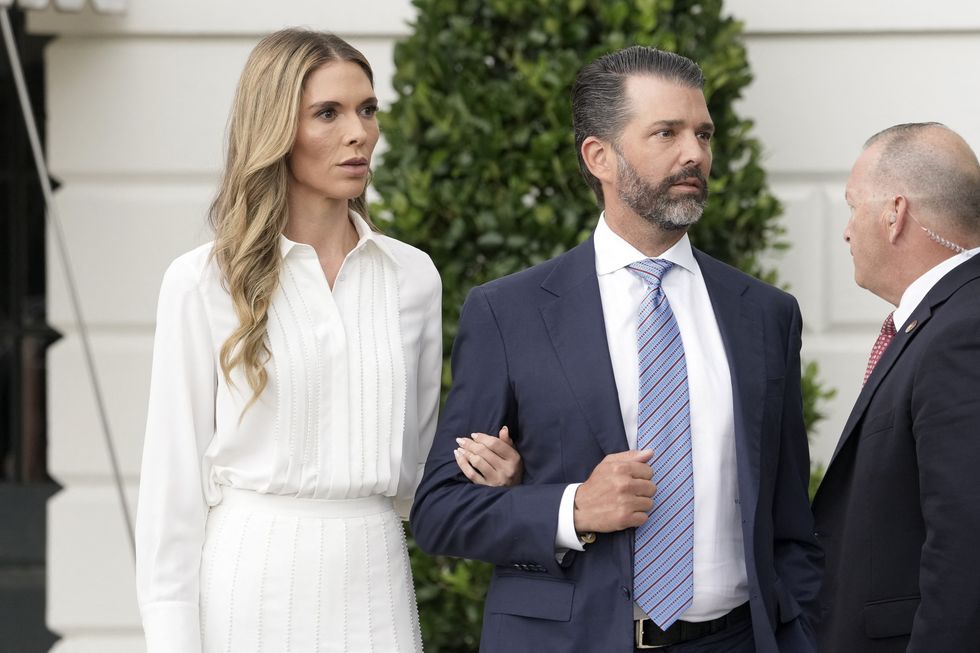  Donald Trump Jr. and Bettina Anderson depart the White House to attend the Military ParadeGetty Images
Donald Trump Jr. and Bettina Anderson depart the White House to attend the Military ParadeGetty Images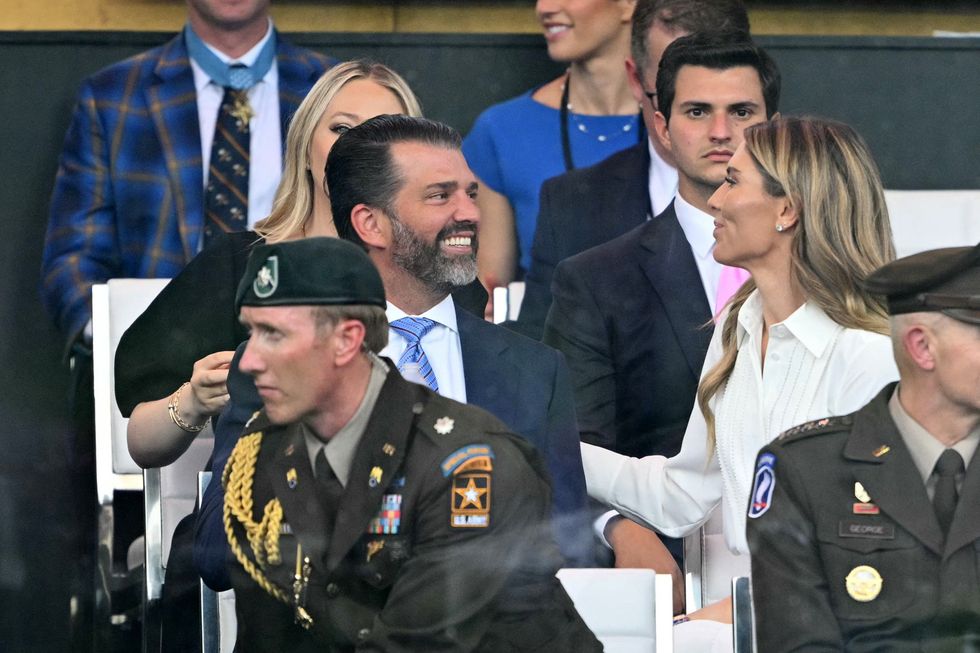  Bettina Anderson and Donald Trump Jr spotted in a candid moment Getty Images
Bettina Anderson and Donald Trump Jr spotted in a candid moment Getty Images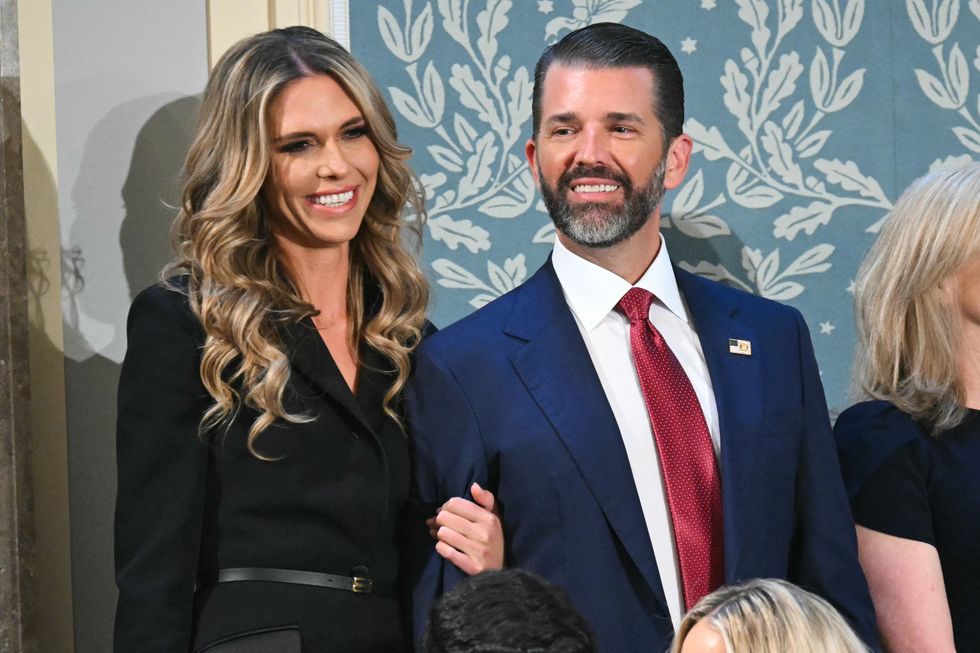  Donald Trump Jr. with Bettina Anderson ahead of US President Donald Trump's addressGetty Images
Donald Trump Jr. with Bettina Anderson ahead of US President Donald Trump's addressGetty Images 
