ISRAEL'S espionage agency Mossad is suspected of having bombed and issued threats to German and Swiss companies that "energetically worked" to aid Pakistan in its nascent nuclear weapons programme in the 1980s, a leading daily said on Tuesday (4).
The Jerusalem Post quoted a prominent Swiss daily report that "the suspicion that Mossad carried out the attacks and issued threats soon arose" after the three bombings in 1981 on three of these companies.
"For Israel, the prospect that Pakistan, for the first time, could become an Islamic state with an atomic bomb posed an existential threat," Swiss daily Neue Zurcher Zeitung (NZZ) reported on Sunday (2).
Pakistan on May 28, 1998, conducted five simultaneous underground nuclear tests at Ras Koh Hills in Chagai district of Balochistan province. Codenamed Chagai-I, it was Pakistan's first public test of nuclear weapons. The second nuclear test, Chagai-II, followed on May 30 in the same year.
Pakistan and Iran worked closely together in the 1980s on developing nuclear weapons devices in which the intensive work of German and Swiss companies is "relatively well researched," NZZ reported.
"New, previously unknown, documents from archives in Bern and Washington sharpen this picture," it claimed.
Swiss historian Adrian Hanni is quoted to have said that Mossad was likely involved in the bomb attacks on Swiss and German companies even though there was no "smoking gun" to prove it.
The Organisation for the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons in South Asia had claimed responsibility for the explosions in Switzerland and Germany.
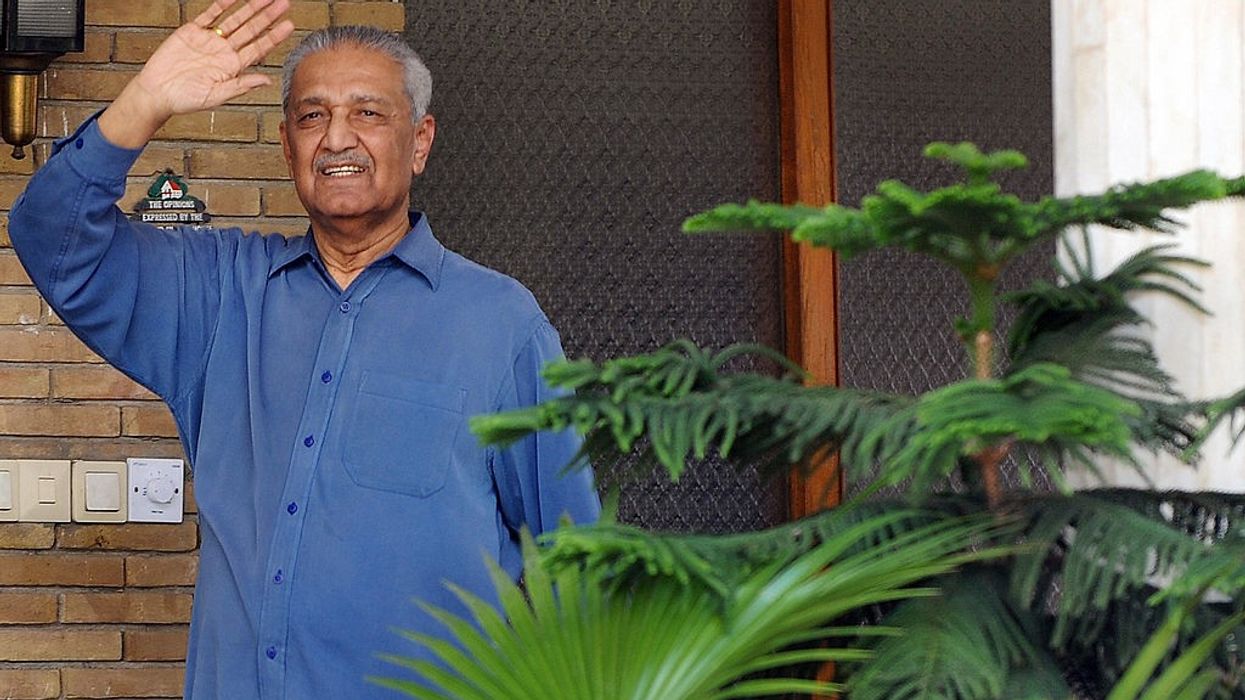
NZZ report also mentions the role of late Pakistan nuclear scientist Abdul Qadeer Khan, who crisscrossed Europe during the 1980s to secure technology and blueprints from Western institutions and companies to develop a nuclear bomb.
Khan is said to have met a delegation of Iran's Organisation for Atomic Energy in 1987 at a Zurich hotel. The Iranian delegation is said to have been led by Engineer Masud Naraghi, the chief of Iran's nuclear energy commission.
Two German engineers, Gotthard Lerch and Heinz Mebus along with Naraghi - who did his PhD in the US - are said to have met Khan's group in Switzerland. Additional meetings reportedly happened in Dubai.
Given Pakistan's "fast-moving efforts" to jumpstart its nuclear weapons programme, the US tried to convince German and Swiss governments to crack down on the aiding companies but was unsuccessful, the report said.
Suspected Mossad agents are then said to have "taken action" against the companies and the engineers involved in aiding Pakistan.
"A few months after the unsuccessful intervention of the American state department in Bonn and Bern, unknown perpetrators carried out explosive attacks on three of these companies - on February 20, 1981, on the house of a leading employee of Cora Engineering Chur; on May 18, 1981, on the factory building of the Walischmiller company in Markdorf and on November 6, 1981, on the engineering office of Heinz Mebus in Erlangen," NZZ reported
"All three attacks resulted in only property damage, and only Mebus' dog was killed," it said.
The explosions are said to have been followed by several phone calls in English and broken German in which strangers threatened other companies.
"The attack that we carried out against the Walischmiller company could happen to you too - this is how the Leybold-Heraeus administration office was intimidated.
Swiss and German companies made huge gains from their association with the Khan nuclear weapons network.
Many of these suppliers, mainly from Germany and Switzerland, soon entered into a business worth millions with Pakistan: Leybold-Heraeus, Wlischmiller, Cora Engineering Chur, Vakuum-Apparate-Technik (VAT, with the chief buyer Friedrich Tinner) or the Buchs metal works, to name a few.
“They benefited from an important circumstance: the German and Swiss authorities interpreted their dual-use provisions very generously: Most of the components that are required for uranium enrichment, for example, high-precision vacuum valves, are primarily used for civil purposes,” NZZ reported.
The National Security Archive in Washington has also recently published diplomatic correspondence from the US State Department from Bonn and Bern in 1980 bringing new information out.
The US seems to have resented the "casual handling of the delicate deliveries to Pakistan" by these two countries.
Bern's behaviour was described by an employee as a "hands-off approach" and the local authorities were accused of "turning a blind eye" on these communications.
(PTI)