In the ever-evolving landscape of travel, a peculiar trend has emerged - last chance tourism. This captivating phenomenon is driven by the allure of experiencing nature's wonders before they vanish forever.
From witnessing the Great Barrier Reef's vibrant corals to encountering polar bears in Churchill, Canada, travellers are flocking to endangered destinations, driven by a sense of urgency.
The genesis of last chance tourism
The concept of last chance tourism first gained prominence in 2008, coinciding with growing concerns about the impact of climate change on our planet's fragile ecosystems. It began in Churchill, Manitoba, where polar bears faced threats due to diminishing sea ice. The term encapsulates the paradoxical nature of travellers seeking out endangered sites, before it’s too late.
The rising trend: Last chance destinations
As budget airlines make global travel more accessible, last chance tourism has seen a surge in popularity. The decline in prices, especially for flights to iconic destinations like Australia's Great Barrier Reef or Argentina's glacier fields, has fueled the urgency to check off items from travellers' "holiday bucket lists."

The environmental conundrum
However, the very act of last chance tourism raises critical questions about its environmental impact. Increased tourist traffic can disturb fragile ecosystems, expose endangered species to poachers, and accelerate environmental degradation. The paradox lies in the fact that the desire to witness nature's splendour 'before it's gone' may inadvertently hasten its demise.
The role of education
Breaking the cycle of self-perpetuating destruction requires education. Studies by the University of Queensland reveal that while 70 per cent of tourists express a strong motivation to witness natural wonders before they disappear, they often underestimate their own contribution to environmental harm.
Small actions, when multiplied, have significant consequences. It's crucial to educate travellers about their role in climate change, habitat destruction, and pollution, fostering a mindset that values small contributions to sustainability.
A global perspective
Last chance tourism is not confined to specific regions; it's a global phenomenon. From the declining health of Australia's Great Barrier Reef to the rapid retreat of glaciers in New Zealand and the vulnerability of Mount Kilimanjaro's snow cover, iconic destinations worldwide face the dual challenge of attracting tourists for economic sustenance while battling environmental threats.
Benefits amidst the crisis
While last chance tourism poses risks, it also offers unique benefits. Tourists seeking these experiences often display heightened environmental consciousness. Their interest may drive increased support for ecotourism and sustainable travel. Furthermore, the economic contributions from nature-based tourism can fund crucial conservation efforts, supporting the protection of vulnerable ecosystems.
The overtourism connection
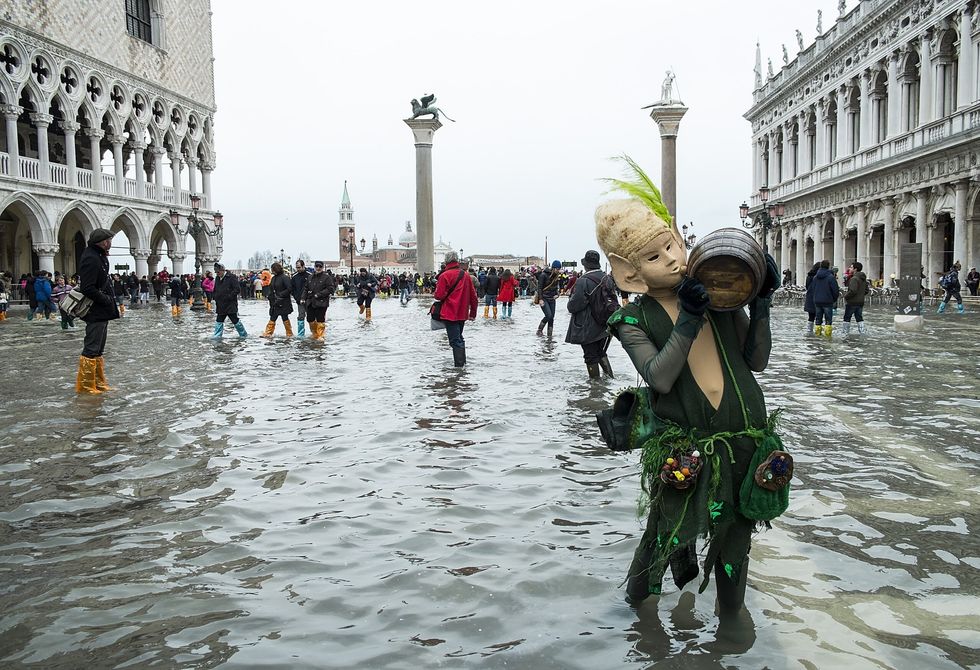
Last chance tourism intersects with the broader issue of overtourism. Destinations already grappling with overcrowding now face the added pressure of last chance tourism. Places like Venice, threatened by flooding, witness a surge in visitors who seek to experience them before they change irreversibly. This synergy creates a destructive duo, further endangering fragile destinations.

Navigating a responsible future
As the tourism industry continues to grow, the responsibility to manage last chance tourism falls on both authorities and individual travellers. Sustainable practices, responsible tourism, and a commitment to minimising environmental impact are essential. While the allure of witnessing vanishing wonders persists, the focus must shift towards preserving these treasures for future generations.
The urgent call for change
The urgency to experience threatened destinations before they disappear should not overshadow the need for responsible travel. Last chance tourism, driven by loss aversion, requires a collective shift in perception.
Industry leaders, media, and travellers must engage in open conversations about the detrimental effects of this trend, fostering a global movement towards responsible tourism.
Last chance tourism is a captivating yet perilous trend that demands introspection. Balancing the desire to witness nature's wonders with the responsibility to protect them is the key to ensuring that our planet's beauty endures.
As travellers, we stand at a crossroads - the choices we make today will determine whether these "last chances" become our legacy or our downfall.



















 NS-31 astronauts celebrate at the crew capsule after a successful flight to spaceBlue Origin
NS-31 astronauts celebrate at the crew capsule after a successful flight to spaceBlue Origin Astronaut Dr. Richard Scott during training at Launch Site OneBlue Origin
Astronaut Dr. Richard Scott during training at Launch Site OneBlue Origin New Shepard booster separates from crew capsule during NS-29Blue Origin
New Shepard booster separates from crew capsule during NS-29Blue Origin Astronaut Gayle King celebrates a successful mission to spaceBlue Origin
Astronaut Gayle King celebrates a successful mission to spaceBlue Origin Astronaut Jesús Calleja at apogeeBlue Origin
Astronaut Jesús Calleja at apogeeBlue Origin Astronaut Elaine Chia Hyde at apogeeBlue Origin
Astronaut Elaine Chia Hyde at apogeeBlue Origin Astronaut Elaine Chia Hyde during training at Launch Site OneBlue Origin
Astronaut Elaine Chia Hyde during training at Launch Site OneBlue Origin New Shepard lifts off from Launch Site One Blue Origin
New Shepard lifts off from Launch Site One Blue Origin The New Shepard booster nears touchdown during NS-29Blue Origin
The New Shepard booster nears touchdown during NS-29Blue Origin New Shepard on the launch pad prior to NS-31Blue Origin
New Shepard on the launch pad prior to NS-31Blue Origin