AN INVESTIGATION has been launched in the northern Indian state of Uttarakhand following media reports that private labs faked Covid-19 tests.
Private labs were hired by the Uttarakhand government to screen visitors for the virus ahead of the Kumbh mela Hindu festival.
The Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) government of Uttarakhand was criticised for organising the festival that attracted millions of people, who went on to infect more people when they returned to their homes after the pilgrimage.
Unmasked visitors were seen at the large Kumbh gathering and days later several parts of India witnessed a peak of the second wave of the virus, with patients struggling to find oxygen cylinders and hospital beds.
'Fake names, mobile numbers, addresses used'
According to media reports, fake names, mobile numbers and addresses were used in more than 100,000 tests conducted during the Kumbh festival in the state in April.
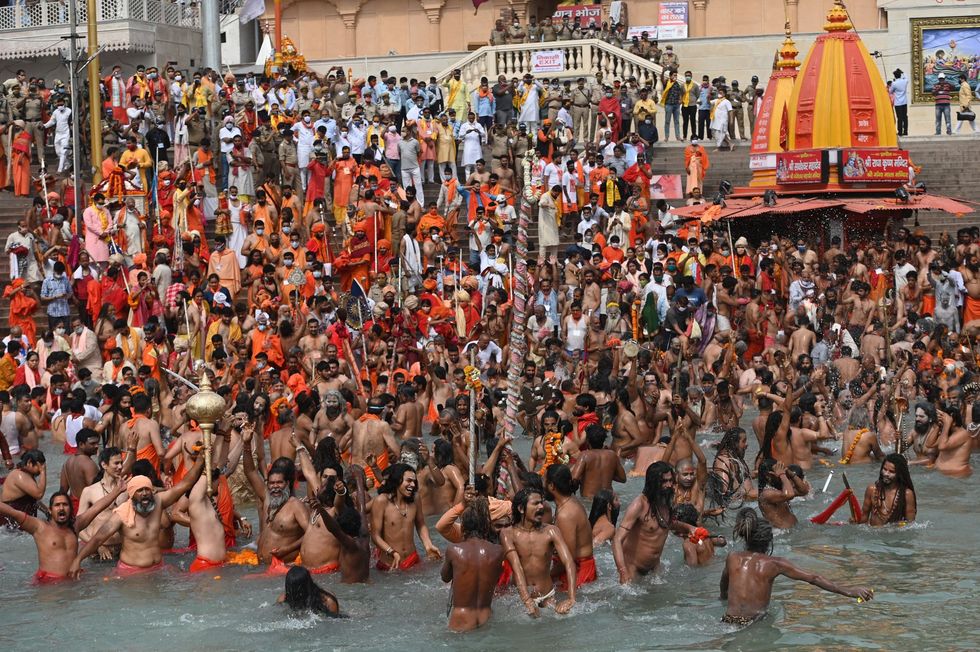

At the time, officials insisted that every visitor was being screened for the disease and private labs in Haryana and Delhi were roped in to conduct a majority of the tests.
Last week, media reports claimed that the labs faked the reports to meet their quota of daily testing and that similar phone numbers and addresses were used in multiple Covid reports.
A spokesperson for the Uttarakhand government, Subodh Uniyal, told ANI news agency that orders have been filed to file a case against the labs that conducted testing at five places in Haridwar during Kumbh.
The Times of India newspaper conducted an investigation and reported on Thursday (17) that a private agency, contracted to carry out Covid testing for the Kumbh Mela, is now under the scanner for conducting 100,000 fake cases. It is alleged that the agency submitted fake office addresses to the Uttarakhand health department and listed phone numbers that are not in use.
Reports of fake Covid tests have also surfaced from Bihar state, where some primary healthcare centres have been accused of providing false data.
In Jamui, Sheikhpura and Patna, government hospitals listed phone numbers as ‘0000000000’ in Covid test reports. Officials have also been accused of taking bribe besides making fake Covid test reports.
In February, Bihar chief minister Nitish Kumar acknowledged the falsification of reports and said the health department would take action against those who were found guilty.
Separately, the Indian government on Wednesday (16) defended its action to increase the gap between two doses of AstraZeneca Covid-19 vaccine up to 16 weeks even though three scientific advisers said there was no agreement over the step.
On Tuesday (15), Reuters reported that the government raised the gap in May without the approval of the scientific group.
The AstraZeneca jab, made locally and branded Covishield, accounts for nearly 90 per cent of the 263 million doses that have been administered in India so far. The opposition has criticised the BJP government asking whether the decision to increase the gap was prompted by a shortage of the vaccine.